What is Diphtheria? An infection caused by a strain of bacteria called Corynebacterium Diphtheriae that can lead to serious complications.
It can affect parts of the respiratory system (parts of the body involved in breathing) and the skin.
It is essential to get treatment as soon as possible as it can be deadly, especially in children who are more vulnerable to the infection.
1. Symptoms: They depend on the affected site and start appearing between 2-5 days following infection.
If the bacteria affects the respiratory system (most common), it can cause:
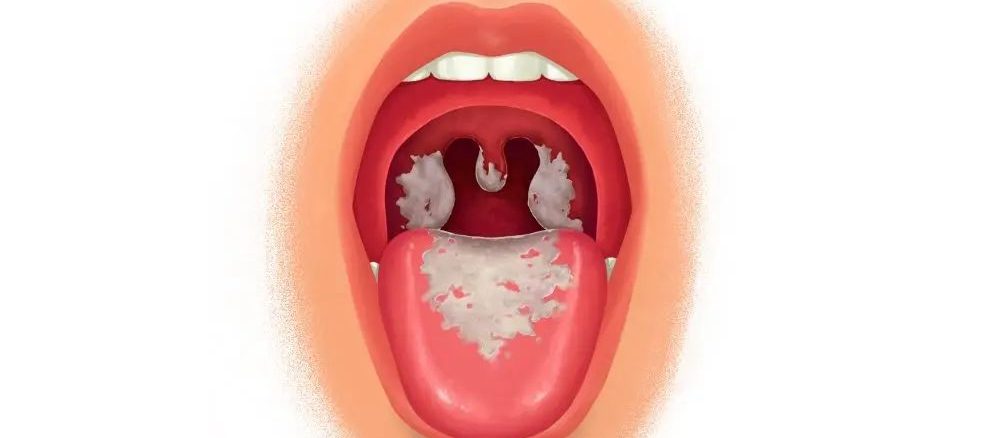
◆ thick grey-white coating that covers the back of the throat, nose, or tongue
◆ sore throat
◆ high temperature
◆ swollen glands in the neck
◆ difficulty breathing and swallowing
If left untreated, it can lead to heart, kidney, and nerve damage.
When the bacteria affects the skin, it will cause the formation of open sores and ulcers. In the case of skin infections, it rarely leads to severe conditions.
2. Causes: It spreads from person to person through respiratory droplets (sneeze or cough) or open wounds. Touching contaminated personal belongings such as used towels or tissues can also lead to its spread.
3. Diagnosis: Based on the presence of common Diphtheria symptoms, a healthcare professional will take a sample from the infected site and test it for the bacteria.
4. Treatment:
◆ Diphtheria antitoxin which stops the bacteria from damaging the body. It is usually used for respiratory Diphtheria infections, and rarely for skin infections.
◆ Antibiotics that kill the bacteria; They are used for both respiratory and skin Diphtheria infections.
After 48 hours of taking antibiotics, infected people are not usually able to spread the bacteria anymore. However, it is essential to continue taking the treatment full course in order to completely kill the bacteria. At the end of the treatment period, the doctor will run tests to ensure the complete removal of the bacteria from the body.
5. Prevention:
◆ Diphtheria vaccination
◆ Close contact with someone infected may require you to take antibiotics to prevent the infection
![]() To stay protected, make sure you are on the lookout for any of those symptoms. If you have any concern, it is best to see a doctor immediately. You can also let us know if you have any questions. Please share with close contacts to increase awareness!
To stay protected, make sure you are on the lookout for any of those symptoms. If you have any concern, it is best to see a doctor immediately. You can also let us know if you have any questions. Please share with close contacts to increase awareness! ![]()